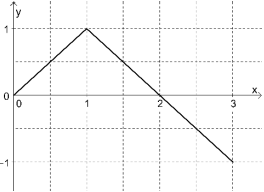
A figura a seguir exibe o gráfico de uma função y = f(x) para 0 ≤ x ≤ 3.
O gráfico de y = [f(x)]2 é dado por
A partir do gráfico do enunciado, tem-se:

Denotando [f(x)]2 por g(x), tem-se:
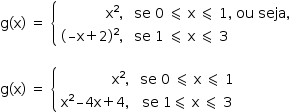
A alternativa que melhor representa o gráfico de g(x) é C.
A figura a seguir exibe o gráfico de uma função y = f(x) para 0 ≤ x ≤ 3.

O gráfico de y = [f(x)]2 é dado por
A partir do gráfico do enunciado, tem-se:

Denotando [f(x)]2 por g(x), tem-se:
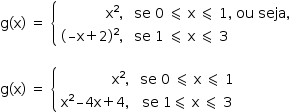
A alternativa que melhor representa o gráfico de g(x) é C.