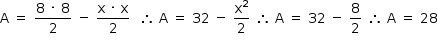• A reta f que passa pelo ponto A(0, 8) e a reta g que passa pelos pontos E(0, –4) e C(4, 0) são perpendiculares e interceptam-se no ponto B, conforme mostra a figura.
• Sendo D(0, 0) a origem do sistema de coordenadas cartesianas, a área do polígono ABCD é
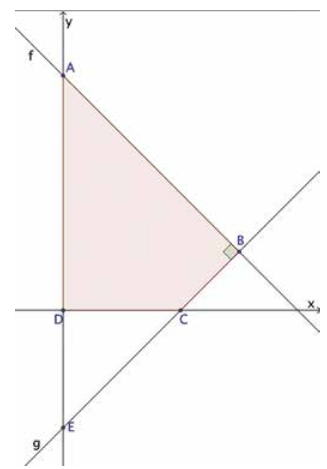
Da figura do enunciado, temos que CD = DE = 4, ou seja, o triângulo CDE é retângulo e isósceles. Logo, as medidas dos ângulos  e
e 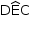 são iguais a 45o e, assim, o triângulo ABE também é retângulo e isósceles, com
são iguais a 45o e, assim, o triângulo ABE também é retângulo e isósceles, com  também medindo 45o.
também medindo 45o.
Como a medida de  é igual a 45o, sendo F o ponto onde o gráfico de f intersecta o eixo x, temos que o triângulo ADF também é isósceles, com AD = DF = 8. O mesmo vale para o triângulo retângulo CBF, em que BC = BF = x.
é igual a 45o, sendo F o ponto onde o gráfico de f intersecta o eixo x, temos que o triângulo ADF também é isósceles, com AD = DF = 8. O mesmo vale para o triângulo retângulo CBF, em que BC = BF = x.
A figura a seguir resume o que foi dito anteriormente:
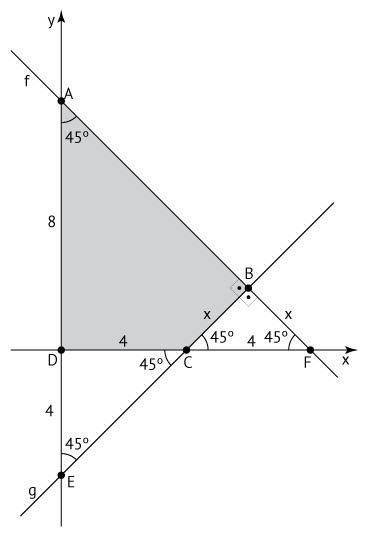
Aplicando o teorema de Pitágoras no triângulo CBF, temos x2 + x2 = 42, ou seja, x2 = 8. A área do polígono ABCD pode ser obtida fazendo-se a área do triângulo ADF menos a área do triângulo CBF, ou seja: